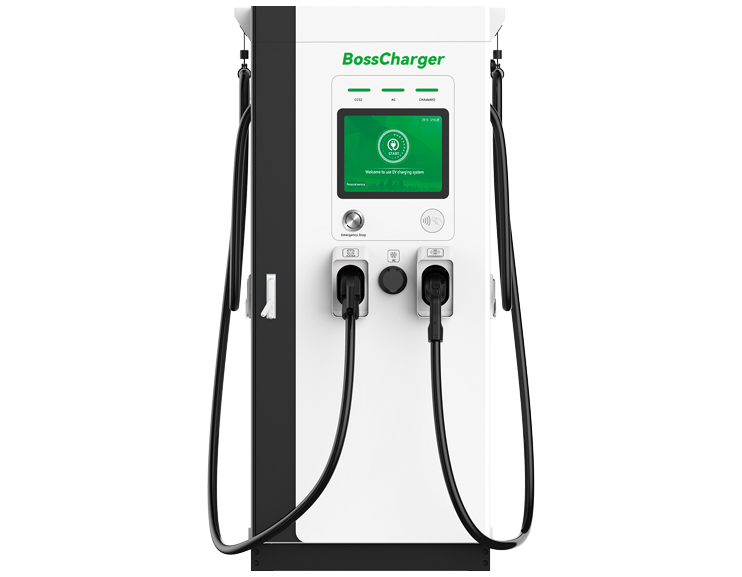
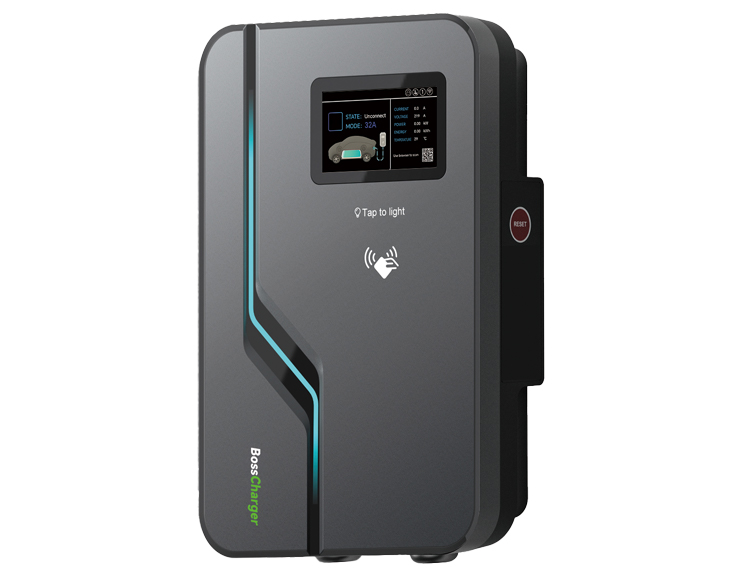
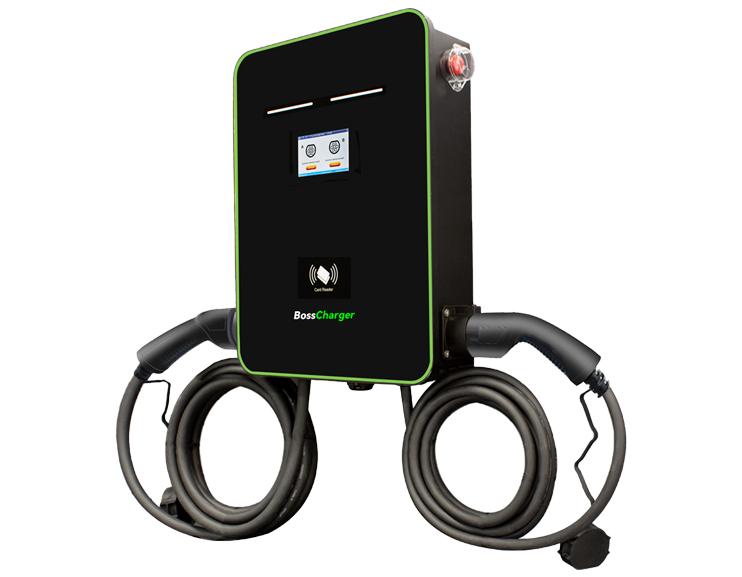
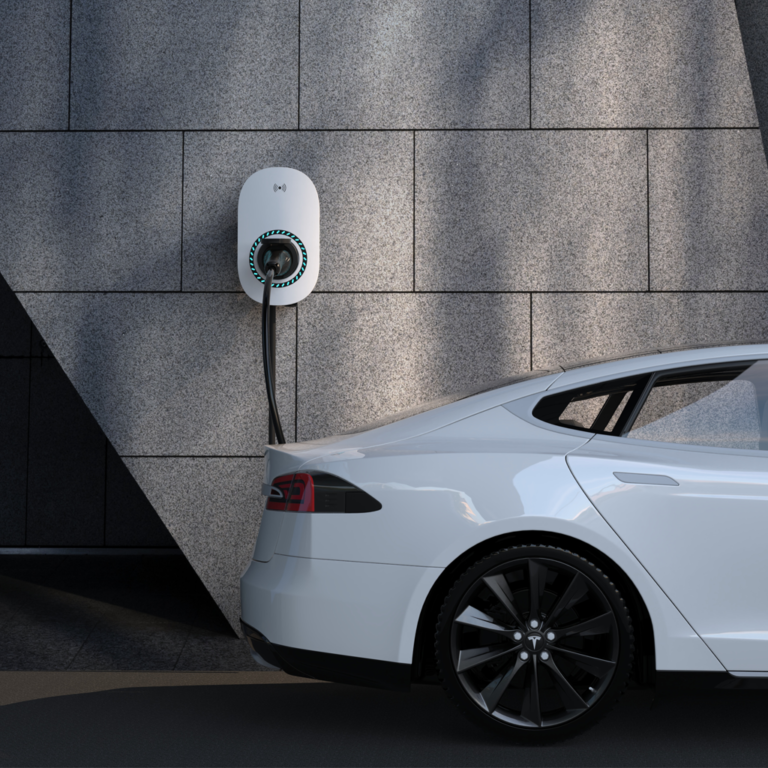
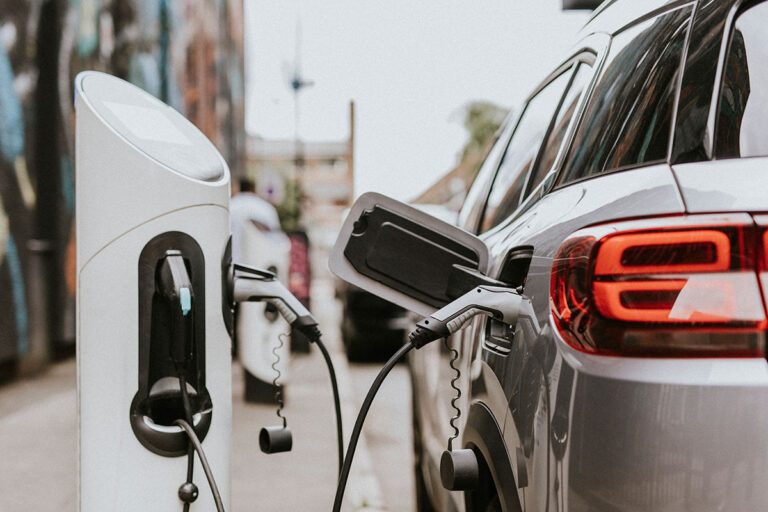
Bosscharger Electric charging station
Smart charging, moving towards the future.
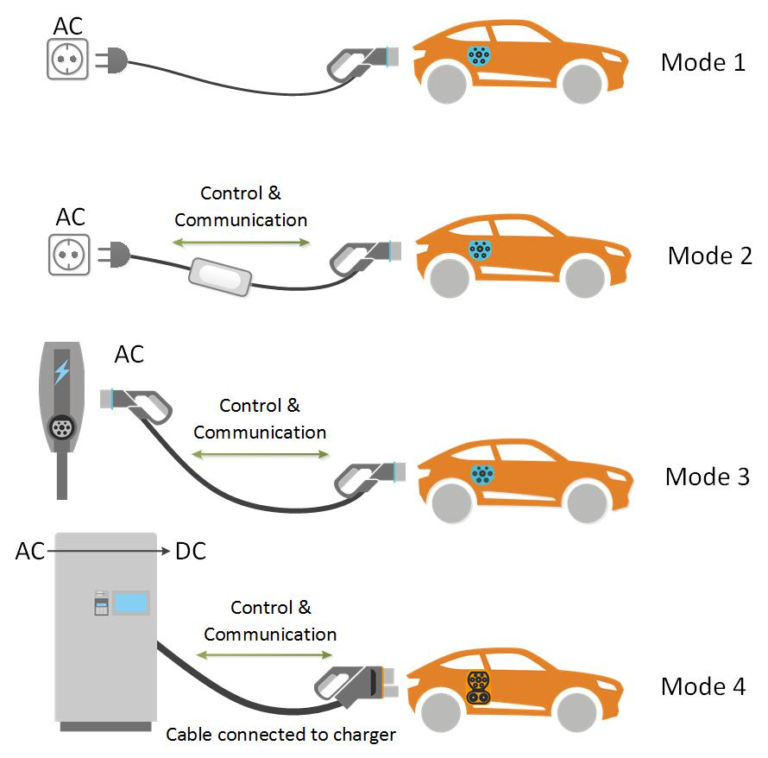
Comprehensive charging solutions to meet your charging needs in multiple scenarios.
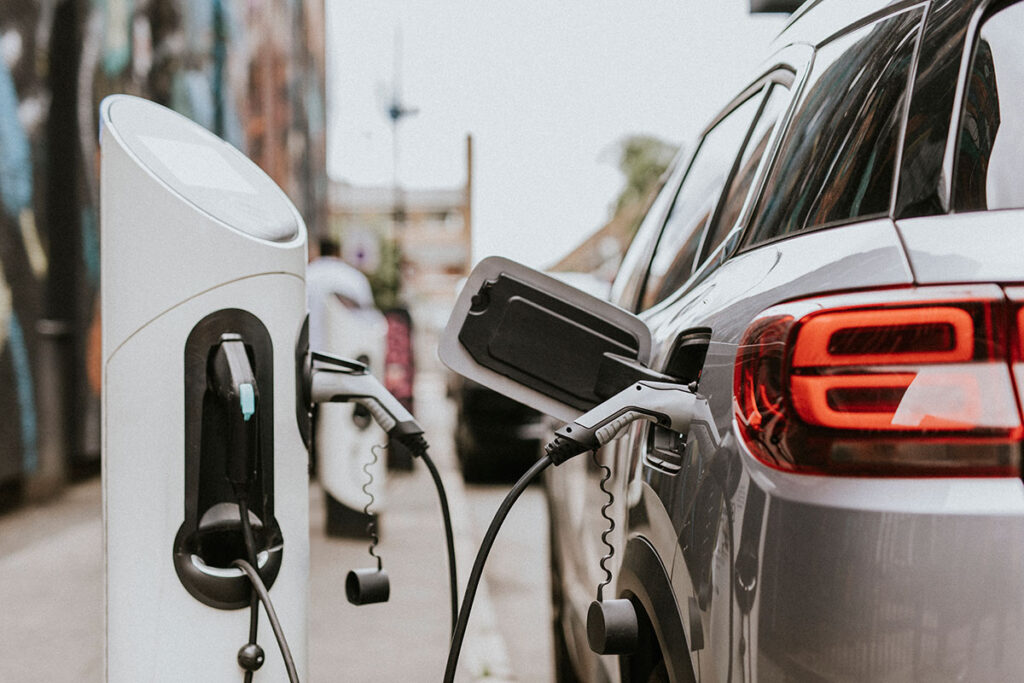



We make driving our clients' success our top priority.EV Charge
Driving customer success is our goal, and we do this through solutions that meet your unique business needs.
We offer a comprehensive solution that includes Bosscharger hardware, software, active charger monitoring, and 24/7 support.
We’re In This Business Since 2020 And We Provide The Best Services.
- We are dedicated to eco-friendly charging solutions that support a greener future.
- Our innovative technology ensures fast, reliable, and accessible charging for all EV users.
- With a focus on customer needs and strong partnerships, we drive the transition to sustainable mobility.

CEO, FOUNDER
The Bosscharger Difference Features
As China's leading charging pile hardware manufacturer, Bosscharger is unique in every way.

Demand Analysis
Our sales staff will discuss your needs with you in depth and then customize a charging pile solution.

Reliable hardware
Self-developed motherboard obtained TUV CE certification

Design capabilities
Support motherboard, appearance, UI, APP and operation platform customization

Complete after-sales service and technical support
5-year extended warranty and localized after-sales support
EV-charging customize
One-stop customized charging pile service.






EV charge Frequently Asked Questions !
Please contact a bosscharger sales representative, we will be happy to answer your questions!
The time required to charge your electric vehicle (EV) depends on several factors. Here's a breakdown to help estimate charging times:
1. Charger Type:
Level 1 (120V AC, household outlet):
Adds 3-5 miles of range per hour.
Example: A full charge for a 60 kWh battery may take 20-40 hours (overnight + most of the day).
Level 2 (240V AC, home/public station):
Adds 20-30 miles of range per hour.
Example: A 60 kWh battery typically charges in 8-10 hours (overnight).
DC Fast Charger (public stations):
Adds 60-100+ miles in 20-30 minutes (varies by vehicle and charger power).
Example: Charging from 10% to 80% might take 20-45 minutes, depending on the EV's max charging rate.
2. Battery Capacity:
Smaller batteries (e.g., 40 kWh Nissan Leaf) charge faster than larger ones (e.g., 100 kWh Tesla Model S).
Example: A 40 kWh battery on Level 2 (~7 kW) takes ~6 hours; a 100 kWh battery on the same charger takes ~14 hours.
3. Vehicle's Onboard Charger:
Limits AC charging speed. For example, if your car maxes at 7 kW, even a 10 kW Level 2 charger won’t exceed 7 kW.
4. State of Charge (SOC):
Charging slows significantly above 80% to protect battery health. The last 20% can take as long as the first 80%.
5. Temperature:
Cold weather can slow charging speeds, especially for DC Fast Charging.
The cost to charge your electric vehicle (EV) one time depends on several factors, including your electricity rate, battery size, and charging location. Here’s a breakdown:
Key Factors Affecting Cost:
Electricity Rate:
Residential rates average 0.12–0.12–0.30 per kWh in the U.S. (varies by state/region).
Public charging stations (e.g., DC Fast Chargers) often cost 0.25–0.25–0.60 per kWh (or more for premium networks).
Battery Capacity:
Example: A 75 kWh battery (e.g., Tesla Model Y) at 0.15/kWhcosts∗∗0.15/kWhcosts∗∗11.25** to fully charge.
Smaller battery (e.g., 40 kWh Nissan Leaf) costs $6.00 at the same rate.
State of Charge:
Charging from 20% to 80% uses less energy than 0–100%. For example, a 75 kWh battery charging 60% (45 kWh) costs **6.75∗∗at6.75∗∗at0.15/kWh.
Charging Location:
Home charging: Cheapest (residential rates).
Public stations: More expensive, especially DC Fast Chargers. Some charge per minute (e.g., 0.20–0.20–0.50/min) instead of per kWh.
The number of miles you can drive on a full electric vehicle (EV) charge depends on your vehicle’s battery capacity and efficiency, as well as driving conditions. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Key Factors Affecting Range:
Battery Capacity (kWh):
Larger batteries store more energy (e.g., 100 kWh Tesla Model S vs. 40 kWh Nissan Leaf).
Vehicle Efficiency:
Measured in miles per kWh (similar to MPG for gas cars). Most EVs get 3–5 miles per kWh.
Example: A 75 kWh battery at 4 miles/kWh = ~300 miles of range.
Driving Conditions:
Highway speeds reduce range (aerodynamic drag).
Cold weather (below freezing) can cut range by 20–30% due to battery chemistry and cabin heating.
Hilly terrain or aggressive acceleration/braking lowers efficiency.
Example EVs and EPA-Estimated Ranges:
| Vehicle | Battery Size | EPA Range (Miles) | Efficiency (mi/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tesla Model S Long Range | 100 kWh | 405 miles | ~4.0 mi/kWh |
| Ford Mustang Mach-E | 91 kWh | 314 miles | ~3.4 mi/kWh |
| Chevrolet Bolt EV | 65 kWh | 259 miles | ~4.0 mi/kWh |
| Hyundai Kona Electric | 64 kWh | 258 miles | ~4.0 mi/kWh |
| Nissan Leaf (base) | 40 kWh | 149 miles | ~3.7 mi/kWh |
Real-World Adjustments:
Cold Weather: Subtract 20–30% from the EPA range.
Example: A 300-mile EV might only achieve 210–240 miles in freezing temperatures.Highway Driving: Sustained speeds above 65 mph reduce range by 10–15%.
Accessories: Using heat, AC, or seat warmers can drain the battery faster.
How to Calculate Your Range:
Check your EV’s battery size (e.g., 75 kWh).
Multiply by its efficiency (e.g., 4 mi/kWh):
75 kWh × 4 mi/kWh = 300 miles.Adjust for conditions (e.g., cold weather: 300 × 0.7 = 210 miles).
Tips to Maximize Range:
Drive at moderate speeds (55–65 mph).
Use eco mode and regenerative braking.
Pre-condition the battery while plugged in (in cold weather).
Keep tires properly inflated.
Summary:
Most modern EVs offer 200–350 miles per full charge, with premium models exceeding 400 miles. Your actual range will vary based on driving style, weather, and terrain. Check your vehicle’s dashboard or app for real-time range estimates tailored to your driving habits!

Recent blogs & insights
Welcome to the bosscharger community, here is everything you want to know.
How Much Energy Does It Take to Fully Charge a Tesla Model Y?
Exclusive agent price support.
20% OFF
exclusive!
Click here to get your exclusive discount !
Please contact our sales manager for exclusive price support.
We have a series of support policies for exclusive agents, and we will work with you to cope with market competition.